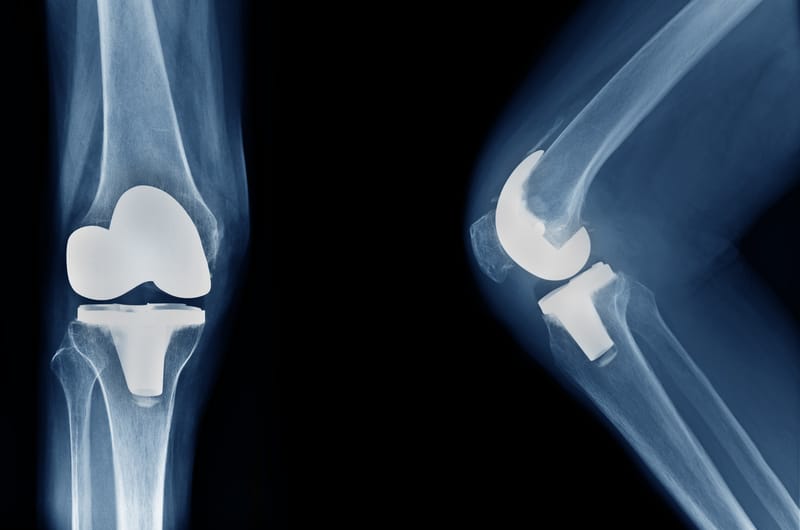
Joint replacement, also known as arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that can help relieve the pain and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis. If nonsurgical treatments like medications, physical therapy, and activity modifications do not relieve your pain and disability, your doctor may recommend total joint replacement. Surgeons perform these procedures using general or regional anesthesia and discuss these options with you prior to surgery to determine the best approach for you.
This procedure involves replacing the damaged cartilage and bone in the knee joint with durable prosthetic parts, eliminating painful movement between the bones and relieving osteoarthritis pain and stiffness. The purpose of arthroplasty is to preserve joint function, and allows you to return to your normal daily activities without chronic pain.
Patients who have thinning of the cartilage but not bone touching bone should not undergo knee replacement surgery, except in rare circumstances.
Your surgeon will suggest either a total or a partial joint replacement
Total joint replacement (total arthroplasty): During a total joint replacement, your surgeon will replace all the parts of your joint with a prosthetic joint.
Partial joint replacement (partial arthroplasty): A partial joint replacement is just what it sounds like. Your surgeon will replace only some parts of your joint. Some healthcare providers sometimes refer to this as joint resurfacing.
Specific types of joint replacement:
• Total Hip Replacement
• Total Knee Replacement
• Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
• Shoulder Joint Replacement
• Reverse Total Shoulder Replacement
• Total Elbow Replacement
• Wrist Joint Replacement (Wrist Arthroplasty)
• Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle